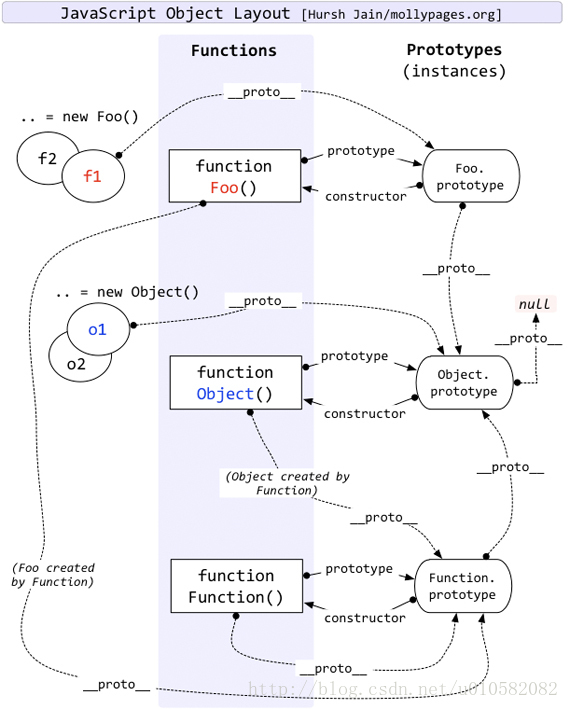
# 原型链
- 每个对象都有__proto__,指向生成该对象的构造函数的原型。
- 函数的__proto__, 指向Function.prototype,
- 构造函数也是函数,构造函数的__proto__, 指向Function.prototype
- Function.prototype属性是一个对象,而对象的__proto__,指向生成该对象的构造函数的原型,所以,Function.prototype._proto_=== Object.prototype
# 1.ES6 extends 继承做了什么操作
- https://juejin.im/post/5c433e216fb9a049c15f841b
- 1.把子类构造函数(Child)的原型(_proto_)指向了父类构造函数(Parent),继承父类的静态方法
- 2.把子类实例child的原型对象(Child.prototype) 的原型(_proto_)指向了父类parent的原型对象(Parent.prototype),继承父类的方法。
- 3.子类构造器里调用父类构造器,继承父类的属性。
# ES6实现继承
// ES6
class Parent{
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
static sayHello(){
console.log('hello');
}
sayName(){
console.log('my name is ' + this.name);
return this.name;
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
constructor(name, age){
super(name);
this.age = age;
}
sayAge(){
console.log('my age is ' + this.age);
return this.age;
}
}
let parent = new Parent('Parent');
let child = new Child('Child', 18);
console.log('parent: ', parent); // parent: Parent {name: "Parent"}
Parent.sayHello(); // hello
parent.sayName(); // my name is Parent
console.log('child: ', child); // child: Child {name: "Child", age: 18}
Child.sayHello(); // hello
child.sayName(); // my name is Child
child.sayAge(); // my age is 18
- 其中这段代码里有两条原型链,不信看具体代码
// 1、构造器原型链
Child.__proto__ === Parent; // true
Parent.__proto__ === Function.prototype; // true
Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true
// 2、实例原型链
child.__proto__ === Child.prototype; // true
Child.prototype.__proto__ === Parent.prototype; // true
Parent.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null; // true
# ES5实现寄生组合式继承
// ES5 实现ES6 extends的例子
function Parent(name){
this.name = name;
}
Parent.sayHello = function(){
console.log('hello');
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log('my name is ' + this.name);
return this.name;
}
function Child(name, age){
// 相当于super
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
// new
function object(){
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F();
}
function _inherits(Child, Parent){
// Object.create
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
// __proto__
// Child.prototype.__proto__ = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
// ES6
// Object.setPrototypeOf(Child, Parent);
// __proto__
Child.__proto__ = Parent;
}
_inherits(Child, Parent);
Child.prototype.sayAge = function(){
console.log('my age is ' + this.age);
return this.age;
}
var parent = new Parent('Parent');
var child = new Child('Child', 18);
console.log('parent: ', parent); // parent: Parent {name: "Parent"}
Parent.sayHello(); // hello
parent.sayName(); // my name is Parent
console.log('child: ', child); // child: Child {name: "Child", age: 18}
Child.sayHello(); // hello
child.sayName(); // my name is Child
child.sayAge(); // my age is 18
# new、Object.create和Object.setPrototypeOf可以设置__proto__
- 模拟实现 new 操作符
- https://juejin.im/post/5bde7c926fb9a049f66b8b52
function newOperator(ctor){
if(typeof ctor !== 'function'){
throw TypeError('not function')
}
newOperator.target = ctor;
var newObj = Object.create(ctor.prototype)
var argsArr = [].slice.call(arguments, 1)
var res = ctor.apply(newObj, argsArr)
if((typeof res === 'object'&& res !== null) || typeof res === 'function'){
return res
}
return newObj;
}
- 模拟实现Object.create()
if(typeof Object.create !== 'function'){
Object.create = function(proto){
function F(){}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F()
}
}
- 模拟实现Object.setPrototypeOf()
`ployfill`
// 仅适用于Chrome和FireFox,在IE中不工作:
Object.setPrototypeOf = Object.setPrototypeOf || function(obj, proto){
obj.__proto__ = proto;
return obj;
}
# 3.
var F = function () {}
Object.prototype.a = function () {}
Function.prototype.b = function () {}
var f = new F()
// 请问f有方法a 方法b吗
1.实例f的原型链:
- f._proto_ === F.prototype; //true
- F.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype; //true
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null; //true
2.构造器F的原型链
- F.prototype.constructor === F; // true
- F._proto_ === Function.prototype; //true
- Function.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype; //true
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null; //true
3.f的__proto__指向F.prototype,F.prototype.__proto__指向Object.prototype,所以f 可以取到a方法, 由于f的原型链上没经过Function.prototype,所以取不到b方法。
4.由于构造函数F是由Function new出来的,所以F.__proto__指向Function.prototype,所以F函数可以取到b方法。
# 4.
function Person(){}
let p1 = new Person()
let p2 = new Person()
let obj = {}
// 写出 p1 p2 Person Function obj Object等的原型链
- 实例p1,p2原型链:
- p1._proto_ === Person.prototype
- p2._proto_ === Person.prototype
- Person.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null
- 构造器Person原型链
- Person._proto_ === Function.prototype
- Function.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null
- 构造器Function原型链
- Function._proto_ === Function.prototype
- Function.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null
- obj原型链
- obj._proto_ === Object.prototype
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null
- 构造器Object原型链
- Object._proto_ === Function.prototype
- Function.prototype._proto_ === Object.prototype
- Object.prototype._proto_ === null